Can You Hack Better Sleep When You Have Kids? I Tried.
Can You Hack Better Sleep When You Have Kids? I Tried.
Overview
With three little kids in the house, getting enough sleep isn’t really up to me. Some nights I’m lucky to make it through without being woken up once or twice. It’s not like I can just decide to sleep more. But I started wondering if I could make the most of the sleep I do get. Could I make it feel deeper, more restorative?
That’s what led me to try the Chilipad from Sleepme. It’s a temperature-controlled mattress pad that’s supposed to help you sleep better by keeping your body at the ideal temperature all night. To add to the benefits, my wife sleeps cold and I sleep warm, so it’s usually hard for us to find a good room and bed temperature for both of us. With the Chilipad “We”, we can set our own sides of the bed to our liking. I figured if I could try to get higher quality, more personalized sleep it would be worth it.
After about a week, I started to feel a difference. I wasn’t waking up as much. I’d open my eyes in the morning and realize I hadn’t stirred once. It felt like I was sleeping harder. Not in a groggy way—more like I was getting pulled into deeper sleep and staying there longer.
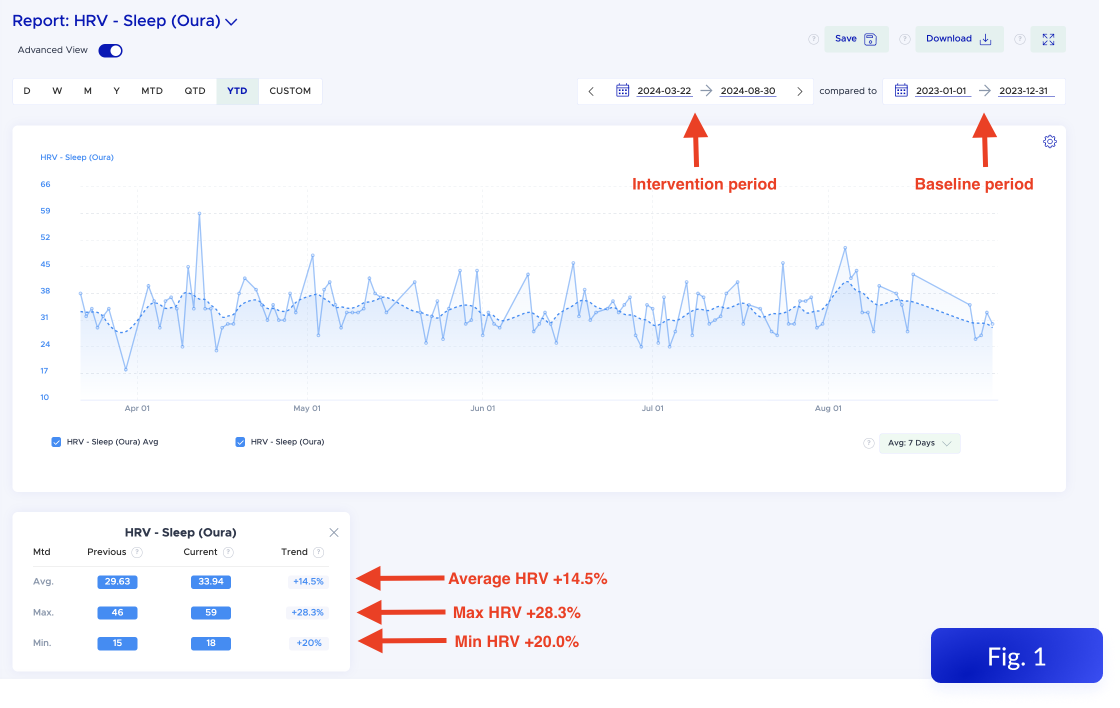
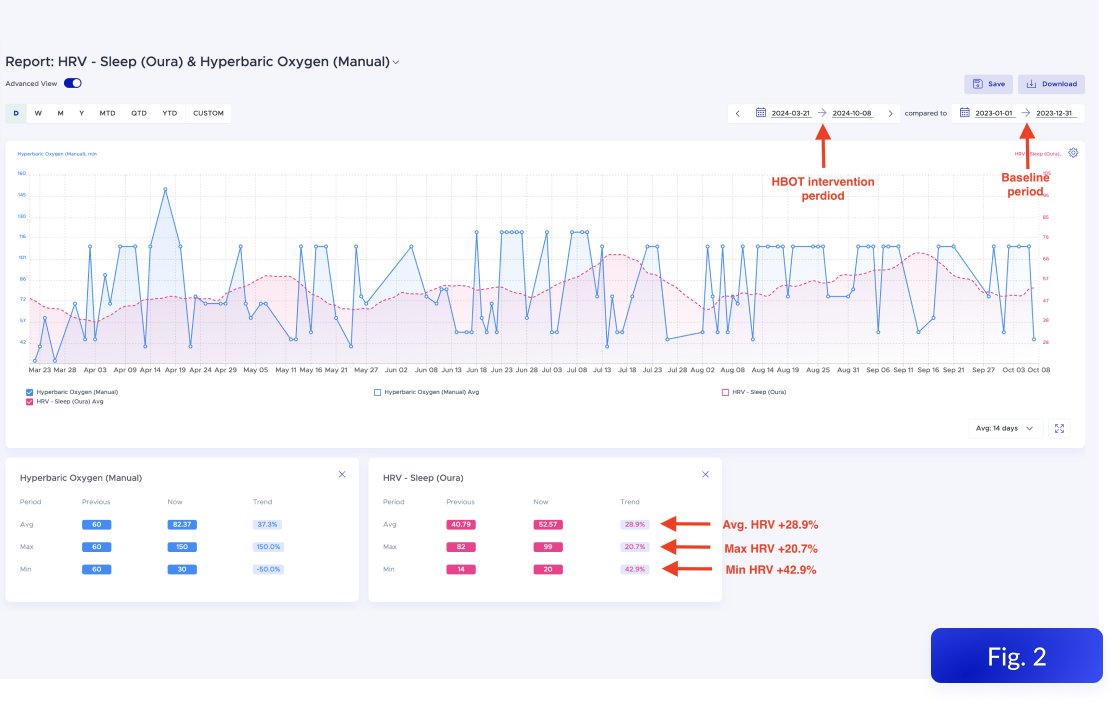
But I didn’t want to just rely on a gut feeling. I’ve been tracking my sleep with Oura for years, and since I also use Heads Up, I could bring in data from the Chilipad Sleep Tracker through Apple Health. Everything came together in one place, which meant I could actually look at the numbers.
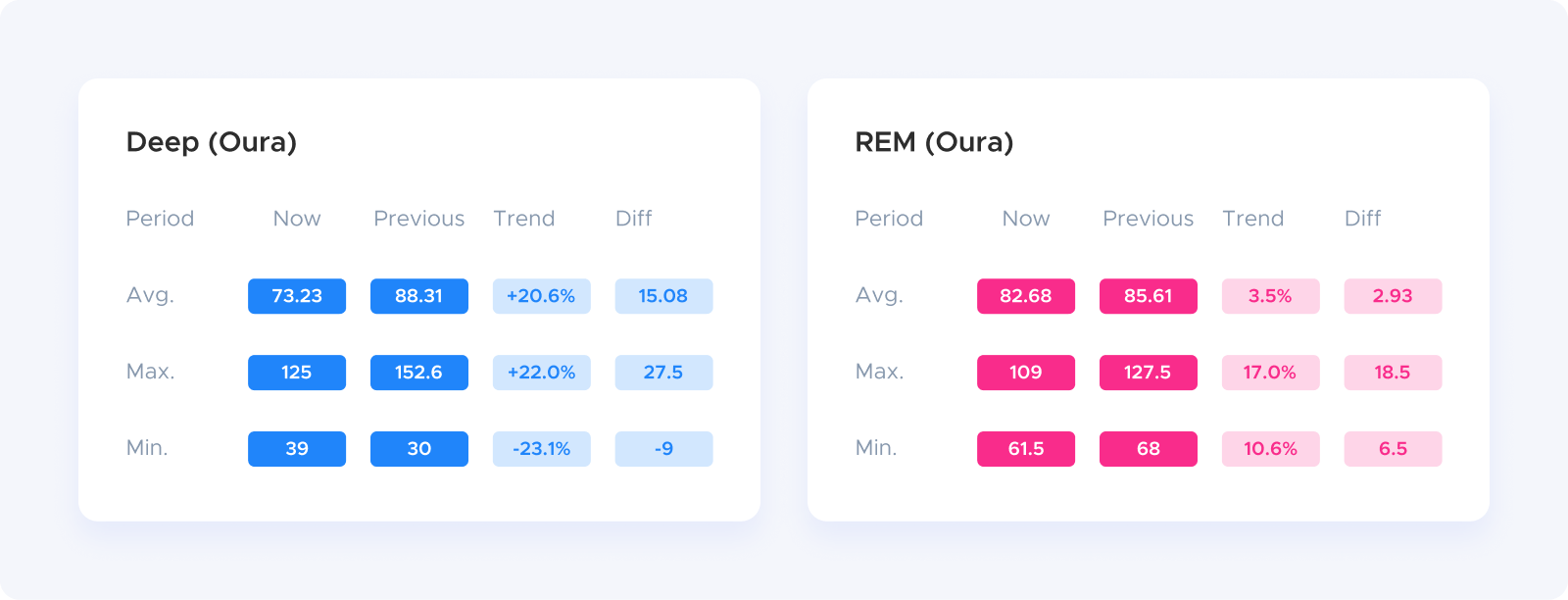
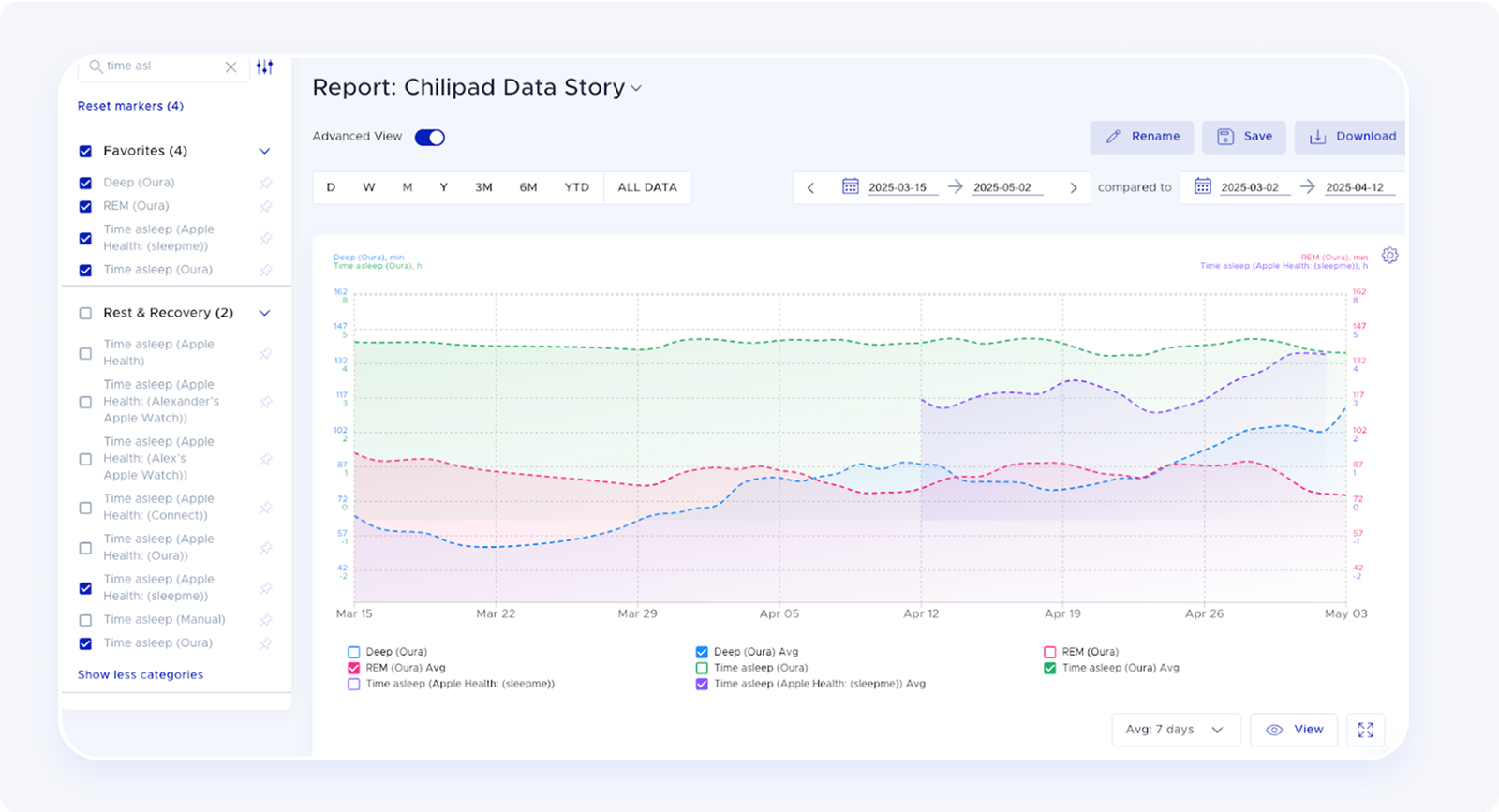
I used the Advanced View in Heads Up Reports to compare the six weeks before I started using the Chilipad to the three weeks after. Since I had consistent data from my Oura Ring during both periods, I could get a clean before-and-after look.
Here’s what the data showed:
-
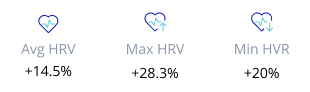
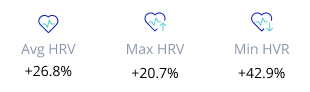
Deep sleep increased by more than 20 percent
-
REM sleep also went up by about 3.5 percent
-
Both types of restorative sleep improved at the same time!
At first, I thought maybe I was just sleeping more overall. That would explain it, right? But when I checked, my total sleep time hadn’t changed at all. I’m still going to bed at the same time. Still getting woken up by the kids before six in the morning. On average, I’m sleeping about six and a half hours a night, just like before.
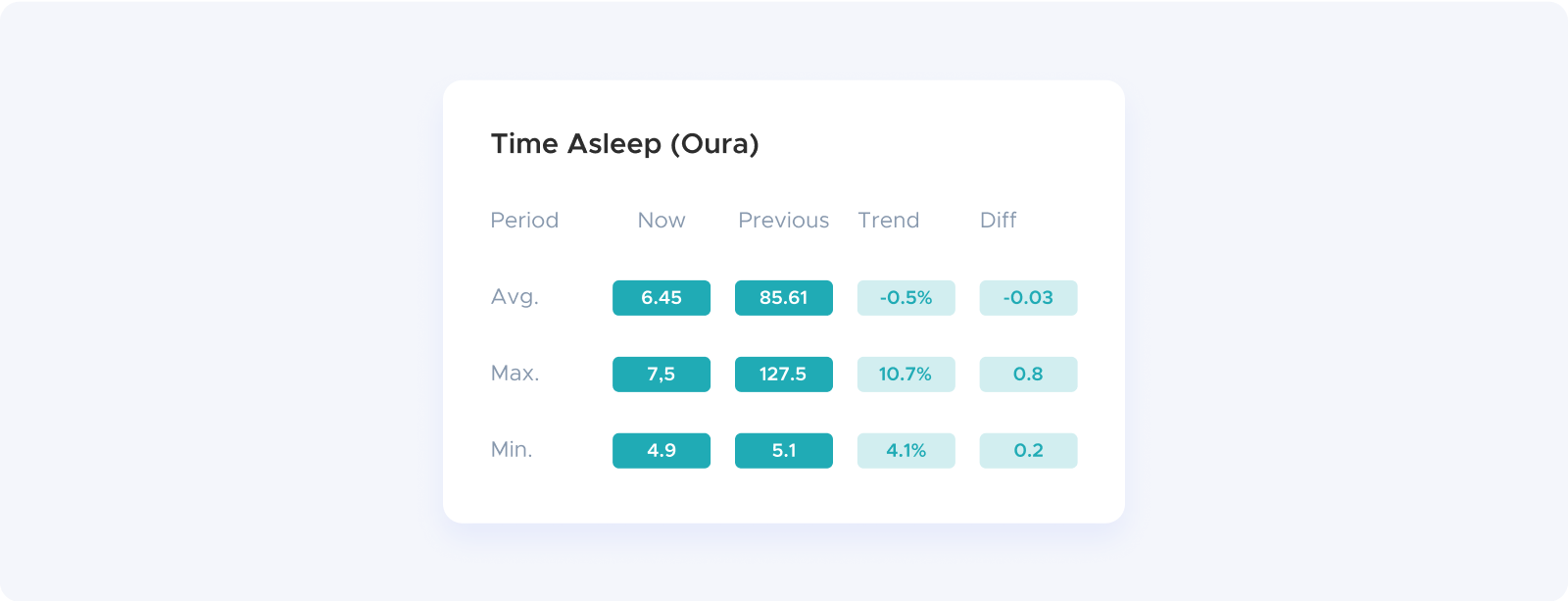
That’s what made the numbers more meaningful. I wasn’t getting more sleep. I was getting better sleep. More of my limited time in bed was going toward the stuff that actually helps you recover.
I saved the report in Heads Up so I could refer back to it later.
Now I’m thinking about trying this with a larger group. Heads Up makes that easy too. Using program management in Heads Up, we can track when someone starts using a sleep mat and create a dashboard that shows changes in sleep quality over time, either for individuals or across a group, using Signals.
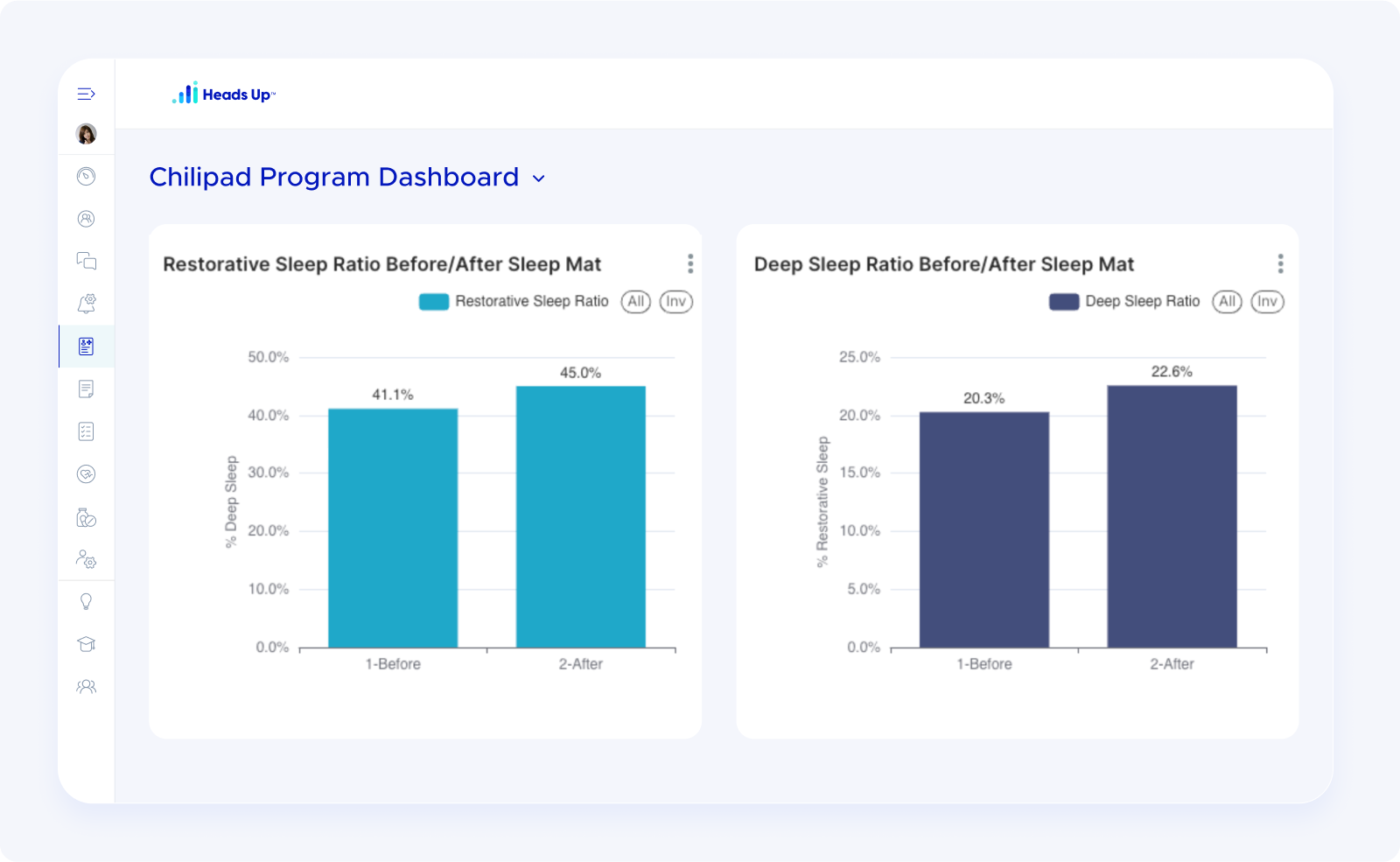 If this holds true for other people, it could be a really compelling sleep improvement strategy for parents, shift workers, or anyone who can’t just add more hours to their night.
If this holds true for other people, it could be a really compelling sleep improvement strategy for parents, shift workers, or anyone who can’t just add more hours to their night.
Tracking Patient Health Data Has Never Been Easier!
Leverage The Power Of Heads Up in your Health Practice
Get started with by scheduling custom demo with one of our specialists to see the difference Heads Up can make in your practice. Schedule your demo and discovery call here.
Optimize Health & Longevity
Synchronize your clients’ medical records, labs, wearables, apps, and more into Heads Up for better outcomes. Sign Up now for a free starter account!